Introduction
In today’s sedentary lifestyle, prolonged sitting has become a norm for many, whether at work, during leisure time, or even during meals. However, what may seem like a harmless habit can actually pose serious risks to our health and well-being. Let’s delve into the health hazards associated with prolonged sitting and explore strategies to mitigate these risks.
Understanding Prolonged Sitting
Prolonged sitting refers to extended periods of sitting or reclining with minimal physical movement. This behavior is prevalent in various settings, including office jobs, commuting, watching TV, and gaming. Despite its widespread acceptance, research has increasingly highlighted the detrimental effects of prolonged sitting on our bodies.
Health Hazards of Prolonged Sitting
- Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases: Prolonged sitting has been linked to an elevated risk of chronic diseases such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain types of cancer. The lack of movement slows down metabolism, reduces calorie burning, and can lead to weight gain and metabolic disturbances.
- Musculoskeletal Issues: Sitting for long periods can cause musculoskeletal problems such as back pain, neck pain, and tightness in the shoulders and hips. Maintaining a static posture for hours on end can strain muscles, ligaments, and joints, leading to discomfort and reduced flexibility.
- Poor Posture: Sitting for prolonged periods often encourages poor posture, characterized by slouching or leaning forward. This can contribute to imbalances in muscle strength and alignment, leading to chronic postural issues and increased risk of injury.
- Reduced Circulation: Remaining seated for extended periods can impede blood circulation, particularly in the lower extremities. Reduced blood flow may contribute to the development of varicose veins, blood clots, and swelling in the legs, increasing the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- Negative Impact on Mental Health: Prolonged sitting has been associated with poorer mental health outcomes, including increased risk of anxiety, depression, and stress. Lack of physical activity can impact neurotransmitter levels and mood regulation, contributing to feelings of lethargy and low energy.
Mitigating the Risks of Prolonged Sitting
- Incorporate Regular Movement: Break up prolonged sitting by incorporating short bouts of movement throughout the day. Stand up, stretch, or take brief walks to promote blood circulation and reduce muscle stiffness.
- Use Ergonomic Furniture: Invest in ergonomic chairs and desks that support proper posture and encourage active sitting. Adjustable furniture allows for customization based on individual needs and preferences.
- Practice Desk Exercises: Perform simple exercises and stretches at your desk to alleviate muscle tension and improve circulation. These may include neck rolls, shoulder shrugs, and seated leg extensions.
- Implement Standing Workstations: Consider using a standing desk or a convertible desk that allows you to alternate between sitting and standing positions. Standing while working can help reduce the negative effects of prolonged sitting on health.
- Take Regular Breaks: Set reminders to take regular breaks from sitting, aiming to stand up and move around at least once every hour. Use breaks to stretch, hydrate, or engage in light physical activity.
THE SEDENTARY EPIDEMIC WELLHEALTHORGANIC.COM:HEALTH-HAZARDS-OF-PROLONGED-SITTING

wellhealthorganic.com:health-hazards-of-prolonged-sitting Sedentary behavior, characterized by prolonged periods of sitting or physical inactivity, has emerged as a significant public health concern. Studies have linked excessive sitting to various health issues, including obesity, cardiovascular diseases, musculoskeletal disorders, and even premature death wellhealthorganic.com:health-hazards-of-prolonged-sitting.
Understanding The Risks
wellhealthorganic.com:health-hazards-of-prolonged-sitting Prolonged sitting increases the risk of developing chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers. The lack of movement slows down metabolism, leading to weight gain and metabolic disturbances. wellhealthorganic.com:health-hazards-of-prolonged-sitting
Impact On Posture And Muscles
Sitting for extended periods can wreak havoc on posture and musculoskeletal health. It puts undue pressure on the spine, leading to postural abnormalities, back pain, and stiffness in the neck and shoulders. wellhealthorganic.com:health-hazards-of-prolonged-sitting
Cardiovascular Complications
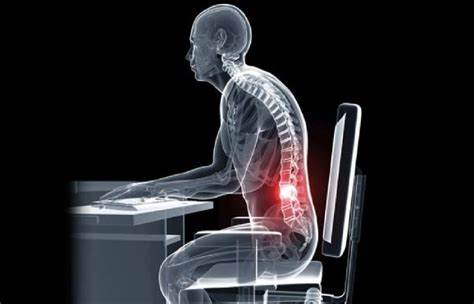
A sedentary lifestyle is closely linked to cardiovascular complications. Prolonged sitting reduces blood flow and impairs circulation, raising the risk of hypertension, stroke, and heart disease.
Metabolic Consequences
Metabolism suffers a significant blow from prolonged sitting. Insulin sensitivity decreases, predisposing individuals to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Moreover, lipid metabolism is adversely affected, leading to elevated cholesterol levels and increased visceral fat deposition.
Psychological Impact
Beyond physical health, prolonged sitting also takes a toll on mental well-being. Studies have linked sedentary behavior to an increased risk of anxiety, depression, and cognitive decline. The lack of physical activity diminishes mood-regulating neurotransmitters, exacerbating stress and mental health issues.
Solutions And Preventive Measures
Combatting the hazards of prolonged sitting requires a multifaceted approach aimed at reducing sedentary behavior and promoting physical activity.
INCORPORATING MOVEMENT BREAKS
Breaking up prolonged sitting with short, frequent movement breaks can counteract its adverse effects. Stand up, stretch, and take a brief walk every hour to improve circulation and alleviate muscle tension.
ERGONOMIC WORKSTATIONS
Investing in ergonomic furniture and accessories can promote proper posture and mitigate musculoskeletal strain. Adjustable desks, supportive chairs, and monitor stands help maintain a neutral spine position and reduce the risk of back pain and discomfort.
REGULAR EXERCISE REGIMEN
Establishing a regular exercise routine is paramount for counterbalancing the sedentary nature of modern lifestyles. Engage in aerobic activities, strength training, and flexibility exercises to improve cardiovascular health, build muscle strength, and enhance overall well-being.
MINDFUL SITTING PRACTICES
Practicing mindfulness while sitting can alleviate the negative effects of prolonged sedentary behavior. Focus on maintaining proper posture, engaging core muscles, and taking deep breaths to promote relaxation and reduce stress on the body.
Conclusion
Prolonged sitting poses significant risks to our physical and mental well-being, contributing to a host of health problems and discomforts. By adopting strategies to reduce sedentary behavior and promote movement throughout the day, we can safeguard our health and vitality. Let’s prioritize incorporating regular activity into our daily routines to counteract the adverse effects of prolonged sitting and cultivate a healthier lifestyle.

